Ear, nose and throat medicine
In addition to the eyes and the sense of touch, the nose and ears are also sensory organs. The sensory cells of the sense of smell are found in the nose. Odour molecules attach themselves to the olfactory receptors of the olfactory cells, which transmit the information to the brain. The approximately ten million olfactory cells are located in the nasal mucosa. There are around 350 different types that bind different odour molecules. Inhaled air is warmed and moistened at the nasal mucosa. An infection of the nasal mucosa - usually with viruses - leads to a cold. This also restricts the sense of smell.
Due to the complicated structures in the head and neck area, a medical speciality, otorhinolaryngology (ENT), has specialised in diseases in this area. In addition to the nose and ears, ENT medicine includes the upper airways, the oral cavity, the pharynx, the larynx, the lower airways and the oesophagus.
Hammer, anvil and stirrup help with hearing
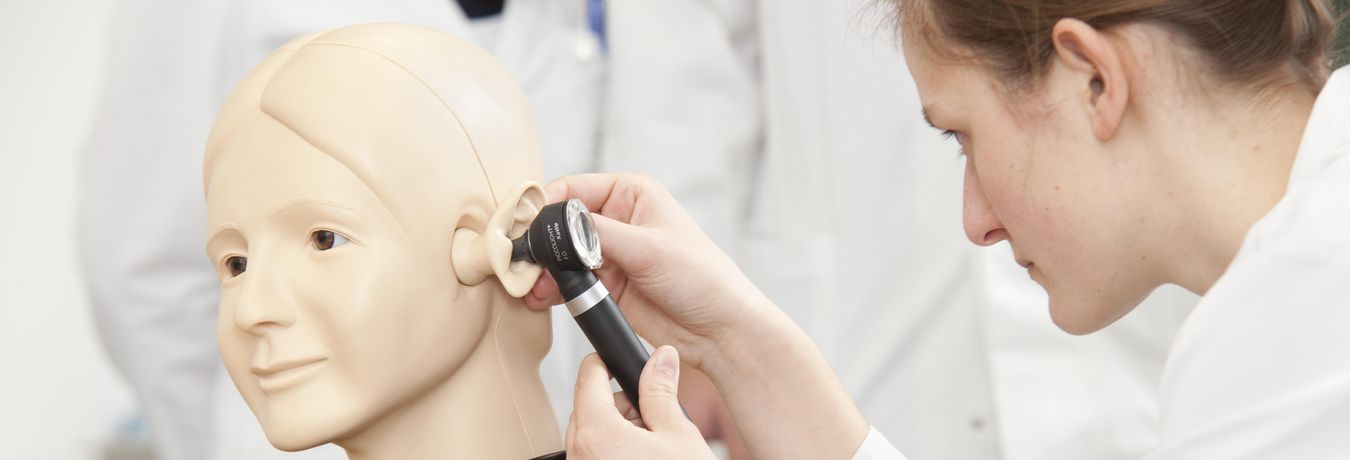
We can perceive tones, sounds and noises with our ears. The outer ear, which includes the pinna and the ear canal up to the eardrum, ensures that sound is focussed and helps with directional hearing. The middle ear consists of the eardrum, the small auditory ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes) and the round window. There is also a connection to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian tube. Sound is mechanically transmitted and amplified in the middle ear. Finally, in the fluid-filled cochlea of the inner ear, hair cells ensure that the sound is picked up and transmitted to the brain via nerve pathways. The inner ear also contains the organ of balance.
16% of adults are hard of hearing
Hearing disorders are among the most common diseases that impair quality of life ("Global Burden of Disease" study, WHO). According to a study from 2017, around 16 per cent of adults in Germany are hard of hearing. Due to demographic trends, the number of people suffering from age-related hearing loss in particular is increasing. Noise-induced hearing loss and hearing impairment due to chronic middle ear infections are among the most common symptoms. If a hearing aid is not sufficient, patients at the Hearing Centre of the University ENT Clinic Ulm can regain their hearing ability through microsurgery on the middle ear or implantable hearing aids.
Tumour board
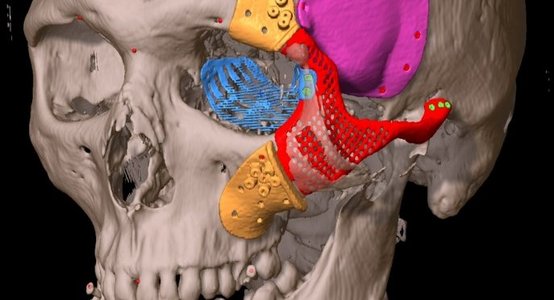
Patients suffering from a head and neck tumour receive interdisciplinary treatment in a certified medical centre under the direction of the ENT Clinic. Surgeons, oncologists, radiotherapists, radiologists and pathologists work out the best possible treatment strategy for each patient in joint case conferences (tumour board).